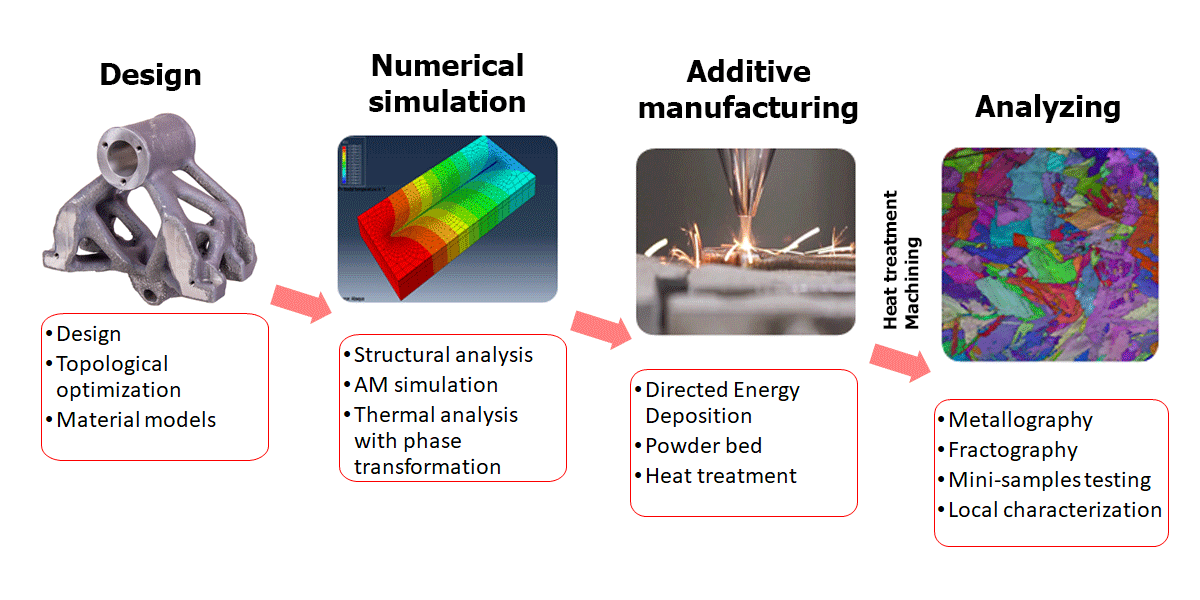
Case study
- practical use is shown in the production of lightweight clamping jaws for drop machine
|

|
Technologies and equipment used
DED (Directed Energy Deposition) – metal printing
Directed energy deposition is a technological process in which the fed material is melted directly at the desired location using a laser beam.
|
InssTek MX600 - DED technology
The InssTek printer uses the so-called Powder-based DED method, where powder is injected into the laser-exposed area and is carried away by an inert gas.
Parameters
- 2kW fiber laser
- 5-axis movement
- Working press 450x600x350mm
- SDM800 (beam diameter 800 µm, layer height 250 µm)
- SDM1600 (1600 µm beam diameter, 600 µm layer height)
- SDM2400 (beam diameter 2400 µm, layer height 900 µm)
- Up to 4 materials at a time
- 3-axis printing capability with preheating to 500°C with 150x150x150mm part size
InssTek MX-LAB – DED technology
Parameters
- 0.5kW fiber IR laser
- 3-axis movement
- Working press 150x150x150mm
- SDM400 (beam diameter 400 µm, layer height 150 µm)
- Up to 4 materials at a time
- Protective atmosphere for the entire chamber
|

Materials
- Stainless steels - 316L, 431L, 420, N700, 15-5PH, 17-4PH, SAF2507, P21 and others
- Tool steels - H13, S2, M2, T15, MS1, 440C
- Titanium – CP Ti, Ti-6-4, Ti-5-5-5-3, Ti-6-2-4-2
- Nickel – IN625, IN713, IN718, IN738, IN780, Hastelloy X, Nimonic 80A
- Cobalt – CoCr F75, Stellite 6, Stellite 21, Stellite 25
- and other
|
Meltio + Fanuc – Wire-Laser metal 3D printing
The Meltio printer uses the Wire-based DED method, where a wire is fed into the laser-exposed area.
|

|
Parameters
- 6x 200W laser bundle
- Coaxial guided wire
- Working area 500x500x1500 mm, larger parts are possible upon consultation
- Head mounted on 6-axis robot + 2-axis table with 500 kg capacity
- Wire diameter 0,8 - 1,2 mm
Materials
- 316L, ER70S, JC100, 17-4PH, H11, 1.4718, 1.2567, IN718, MoNiCr, Ti6Al4V
|
LPBF (Laser Powder Bed Fusion) – metal printing
An even layer of powder is applied to the vertically adjustable table and then the area corresponding to the cross-section of the desired piece is melted by a laser beam. Gradual application of individual cuts achieves the desired shape.
|
Aconity TWO – PBF technology
Parameters
- 2x 1kW nLight SM fiber laser
- Building space dia.400x400 mm
- Reduced chamber dia.140x120 mm
- Layer thickness: from 30 μm to 120 μm
- Minimum x/y resolution: 80 μm (up to 500 μm)
- Double-sided powder deposition
- Preheating 500°C for dia.350x200 mm and reduced chamber
Materials
- 316L, 1.2709, AlSi10Mg, Ti6-4, CuCr1Zr, CoCrMo, IN718, H11
|

|
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) – plastic printing
This is the most available method of 3D printing, where a plastic string is melted and this melt is extruded by a nozzle and gradually laid by lining into individual layers.
|
 |
miniFactory Ignite
- Working space 400x600x400 mm
- Version with two nozzles, the second one can be used for supports
- Layer thickness 0.1-0.3 mm for 0.4 mm nozzle
- Nozzles: 0,4; 0,6; 1,0 mm
- Preheating of the working chamber up to 200 °C
- Chamber heating for fillets
- Materials: ABS, ASA, PC, PA6, PA11, ULTEM 9085
Průša XL
- Working space 360x360x360 mm
- Version with two printing heads, the second can be used for supports
- Layer thickness 0.1-0.3 mm for 0.4 mm nozzle
- Materials: PLA, PETG, ASA, ABS, FLEX, PC Blend, and more
|